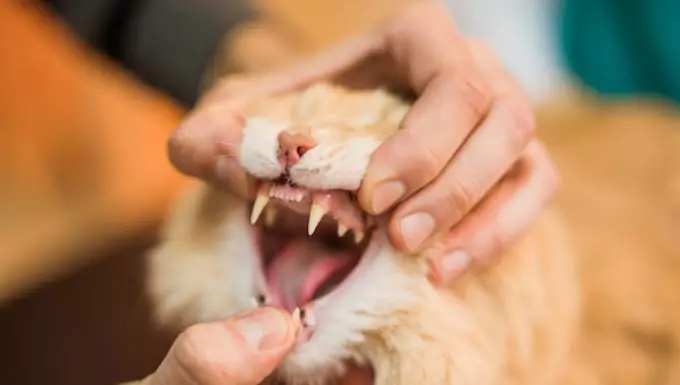
Gingival hyperplasia, commonly referred to as enlarged gums, is a condition in cats characterized by the inflammation of gingival tissue. This ailment often arises as a result of bacterial presence and plaque accumulation in the mouth. While it can be alarming for pet owners to witness their feline companions suffering from this issue, it is largely preventable through diligent dental care practices. Awareness and proper management of this condition can vastly improve a cat’s quality of life.
Several signs manifest when a cat suffers from gingival hyperplasia. Symptoms that owners should be vigilant for include inflamed gums, increased gum thickness, excessive drooling, formation of abnormal growths along the gum line, and the presence of pus around the teeth. Behavioral changes, such as irritability or discomfort when eating, may also be observed. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely veterinary intervention and can aid in avoiding more serious consequences.
The primary culprits behind this condition are bacteria and plaque buildup; however, additional factors can exacerbate the situation. Poor dental hygiene is at the forefront, often aggravated by a low-quality diet high in sugars and fillers. Moreover, a cat’s age, inherent diseases, and even specific breeds predisposed to dental problems can contribute to gingival hyperplasia. Owners should ensure they maintain their cats’ dental hygiene and be aware of how these risk factors apply to their pets.
When a cat presents symptoms of gingival hyperplasia, a visit to the veterinarian is essential. The initial step in diagnosis involves a thorough discussion about the cat’s symptoms and medical history, focusing particularly on breed-related health issues. A comprehensive oral examination follows, potentially supplemented by X-rays to capture detailed images of the gums and roots of the teeth. In some cases, veterinarians may conduct biopsies of any significant growths, helping to ensure an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approach.
Treatment for gingival hyperplasia typically begins with a professional dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from the gums and teeth. Pain relief medications are often prescribed to ensure the comfort of the affected cat. Pet owners must adhere strictly to the veterinarian’s instructions regarding medication dosage and duration to facilitate a successful recovery. In the event of serious cases, surgical intervention may be recommended to correct the gum line and remove excessive tissue.
Prevention is always preferable to treatment, particularly with gingival hyperplasia. Implementing a routine dental care regimen can significantly decrease the chances of this condition developing. Regular brushing, providing dental treats, and scheduling routine veterinary dental check-ups are vital steps in promoting good oral health for cats. As responsible pet owners, it is our duty to ensure our furry friends enjoy a healthy, pain-free life by being proactive in their dental care.
Understanding the complexities of gingival hyperplasia in cats not only assists in timely diagnosis and effective treatment but also highlights the importance of maintaining excellent dental hygiene as a preventative measure.